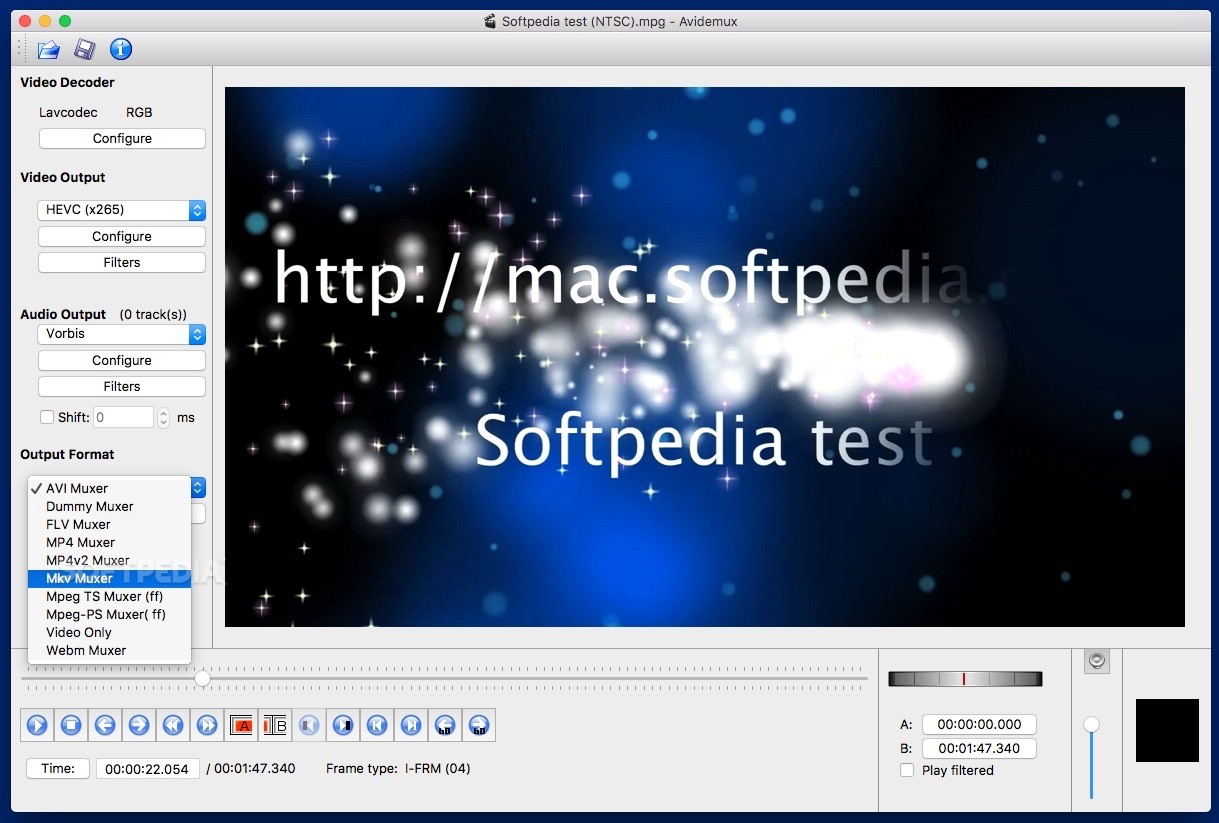
1) Download and install the Avidemux 2.6 convertor app (here is a link). 2) Open the Avidemux program. 3) Click the 'File' menu item, then 'Open' and choose the WMV video file. 4) Under the 'Video Output' block of settings, in the left, in the dropdown list, choose 'Mpeg4 AVC (x264)'. 5) This will enable the 2 next options. Update: Sometimes while trying to fix a MP4 file, though you might be able to successfully fix it and play it in ‘Avidemux', the corrected sync value might simply be lost, after saving it into a new MP4. If this occurs, then I advice you to try selecting ‘ MP4v2 Muxer ‘ rather than using the ‘ MP4 Muxer ‘ (under ‘ Output Format ‘).
| Developer(s) | 'Mean', 'Gruntster' and 'Fahr'[1] |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 2.7.8 (9 March 2021; 2 months ago[2]) [±] |
| Preview release | None [±] |
| Repository | |
| Written in | C++ |
| Operating system | Windows, OS X, Linux, BSD |
| Platform | IA-32 and x64 |
| Available in | English, Czech, French, Italian and German |
| Type | Video editing software |
| License | GNU General Public License |
| Website | avidemux.org |
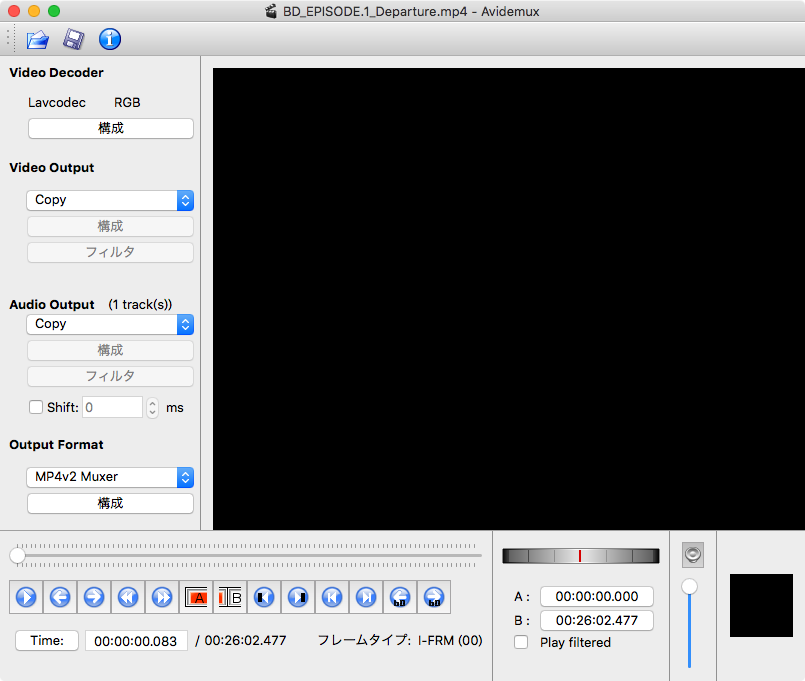
Avidemux is a free and open-source software for non-linear video editing and transcoding multimedia files. The developers intend it as 'a simple tool for simple video processing tasks' and to allow users 'to do elementary things in a very straightforward way'.[3] It is written in C++ and uses Qt for its graphical user interface, and FFmpeg for its multimedia functions. Starting with version 2.4, Avidemux also offers a command-line interface, and since version 2.6, the original GTK port has not been maintained and is now discontinued.
Avidemux is developed for Linux, macOS, and Windows. Unofficial builds are also available for FreeBSD, NetBSD, and OpenBSD.[4][5][6]
Features[edit]
Avidemux is capable of non-linear video editing, applying visual effects (called 'Filters' by Avidemux) to video, and transcoding video into various formats. Some of the filters were ported from MPlayer and Avisynth. Avidemux can also insert audio streams into a video file (an action known as multiplexing or 'muxing') or extract audio streams from video files (an action known as 'demuxing').
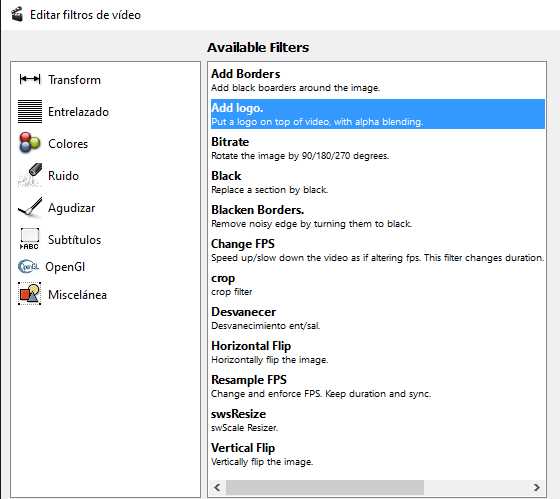
Avidemux Mp4 Vs Mp4v2
An integral and important part of the design of the program is its project system, which uses the SpiderMonkey JavaScript engine. Whole projects with all options, configurations, selections, and preferences can be saved into a project file. Like VirtualDub's VCF scripting capabilities, Avidemux has advanced scripting available for it both in its GUI and command line modes. It also supports a non-project system just like VirtualDub, where users can simply create all of their configurations and save the video directly without making a project file. A project queue system is also available.
Avidemux has built-in subtitle processing, both for optical character recognition of DVD subtitles and for rendering hard subtitles. Avidemux supports various subtitle formats, including MicroDVD (.SUB), SubStation Alpha (.SSA), Advanced SubStation Alpha (.ASS) and SubRip (.SRT).
Components[edit]
Avidemux was written from scratch, but additional code from FFmpeg, MPlayer, Transcode and Avisynth has been used on occasion as well. Nonetheless it is a completely standalone program that does not require any other programs to read, decode, or encode other than itself. The built-in libavcodec library from the FFmpeg project is used for decoding and encoding of various audio and video formats such as MPEG-4 ASP. The primary (though not the only) Avidemux programmer uses the nickname 'Mean' on the Avidemux forum.[7]

Multithreading[edit]
Multithreading has been implemented in the following areas of Avidemux (some partially through libavcodec):
- Encoding
- MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 (using libavcodec)
- MPEG-4 Part 2 SP/ASP (using libavcodec or Xvid)
- Earlier versions of Xvid are not compatible with this feature.
- H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 AVC (using x264)
- H.265/HEVC (using x265)
- Decoding
- MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 (using libavcodec)
- MPEG-4 Part 2 SP/ASP (using libavcodec)
Supported formats[edit]
Avidemux Mp4v2
Avidemux supports following file formats:
| Name | File extension | As input | As output |
|---|---|---|---|
| Audio Video Interleave | .AVI | Yes | Yes |
| Advanced Systems Format | .ASF, .WMV and .WMA | Yes | No |
| Flash Video | .FLV | Yes | Yes |
| Matroska | .MKV | Yes | Yes |
| MPEG elementary stream | N/A | Yes | No |
| MPEG program stream | .MPG and .MPEG | Yes | Yes[a] |
| MPEG transport stream | .TS | Yes | Yes |
| MPEG-4 Part 14 | .MP4 | Yes | Yes |
| NuppelVideo | .NUV | Yes | No |
| OGM | .OGM | Yes | Yes |
| QuickTime | .MOV | Yes | No |
| 3GP | .3GP | Yes | No |
| DVD-Video | .VOB | Yes | Yes |
| WebM | .WebM | Yes | Yes |
| Name | As input | As output |
|---|---|---|
| AV1 | Yes[b] | No |
| Cinepak | Yes | No |
| DV | Yes | Yes |
| FFV1 | Yes | Yes |
| H.263 | Yes | Yes |
| H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 AVC | Yes | Yes[c] |
| H.265/HEVC | Yes | Yes[d] |
| HuffYUV | Yes | Yes |
| MPEG-1 | Yes | Yes |
| MPEG-2 | Yes | Yes |
| MPEG-4 Part 2[e] | Yes[f] | Yes[g] |
| Motion JPEG | Yes | Yes |
| MSMPEG-4 v2[h] | Yes | No |
| Raw video – RGB | Yes | No |
| Raw video – YV12 | Yes | Yes |
| Snow | No | Yes |
| Sorenson Video 3 (SVQ3) | Yes | Yes |
| VC-1[i] | Yes | No |
| VP3 | Yes | No |
| VP6 | Yes[j] | No |
| VP8 | Yes[j] | No |
| VP9 | Yes[j] | Yes[k] |
| Windows Media Video 8[l] | Yes | No |
| Y800 | Yes | Yes |
| Name | As input | As output |
|---|---|---|
| Adaptive Multi-Rate – Narrow Band (AMR-NB) | Yes | No |
| Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) | Yes | Yes |
| AC-3 | Yes | Yes |
| DTS | Yes | No |
| Linear pulse-code modulation (LPCM) | No | Yes |
| MP2 | Yes | Yes |
| MP3 | Yes | Yes |
| Opus | Yes | Yes |
| Pulse-code modulation (PCM) | No | Yes |
| Vorbis | Yes | Yes |
| Name | File extension | As input | As output |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows bitmap | .BMP | Yes | No |
| JPEG | .JPG and .JPEG | Yes | No |
See also[edit]
Notes[edit]
- ^Can create files that are compatible with Video CD, SVCD or DVD Video
- ^Using libaom
- ^Using x264
- ^Using x265
- ^Both Simple Profile and Advanced Simple Profile
- ^Supported codec FourCCs: DIVX, DX50, XVID, FMP4, M4S2
- ^Using FFmpeg or Xvid
- ^FourCC: DIV3
- ^FourCC: WMV3
- ^ abcThrough libavcodec
- ^Using Libvpx
- ^FourCC: WMV2

References[edit]
- ^Avidemux 2.5 Change Log (included with the Avidemux 2.5.5 for Windows)
- ^'Avidemux 2.7.8'. SourceForge. Dice Holdings. Retrieved 15 July 2020.
- ^Avidemux developers (12 November 2012). 'Avidemux Quickstart'. avidemux.org. Archived from the original on 12 September 2020. Retrieved 12 September 2020.
Avidemux is a simple tool for simple video processing tasks. The keyword here is simple: it does not offer tools like a timeline, multitrack editing, you cannot freely move or splice audio and video clips from various sources. However, Avidemux allows you to do elementary things in a very straightforward way.
- ^'FreeBSD Avidemux port'. Archived from the original on 15 April 2013. Retrieved 2 July 2010.
- ^'The NetBSD Packages Collection: multimedia/avidemux'. Retrieved 2 July 2010.
- ^'OpenBSD Packages'. Archived from the original on 10 February 2010. Retrieved 2 July 2010.
- ^'Messages by 'Mean''. Avidemux forum. Retrieved 19 November 2011.
- ^ ab'Supported input formats'. Avidemux wiki documentation. Avidemux. 16 April 2010. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^ ab'Supported output formats'. Avidemux wiki documentation. Avidemux. 15 April 2010. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^'Video decoders'. Avidemux wiki documentation. Avidemux. 16 April 2010. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^'Video encoders'. Avidemux wiki documentation. Avidemux. 15 April 2010. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^'Audio decoders'. Avidemux wiki documentation. Avidemux. 16 April 2010. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^'Audio encoders'. Avidemux wiki documentation. Avidemux. 15 April 2010. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
Further reading[edit]
- Rankin, Kyle (2006). Linux Multimedia Hacks. O'Reilly Media, Inc. pp. 189–190, 221–222. ISBN978-0-596-10076-6.
- Montabone, Sebastian (2010). 'Chapter 10: Movie Editing'. Beginning Digital Image Processing: Using Free Tools for Photographers. Apress. pp. 235–253. ISBN978-1-4302-2841-7.
External links[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Avidemux. |
Avidemux Mp4 Mp4v2
Avidemux is a free and open-source software for non-linear video editing and transcoding multimedia files. The developers intend it as 'a simple tool for simple video processing tasks' and to allow users 'to do elementary things in a very straightforward way'.[3] It is written in C++ and uses Qt for its graphical user interface, and FFmpeg for its multimedia functions. Starting with version 2.4, Avidemux also offers a command-line interface, and since version 2.6, the original GTK port has not been maintained and is now discontinued.
Avidemux is developed for Linux, macOS, and Windows. Unofficial builds are also available for FreeBSD, NetBSD, and OpenBSD.[4][5][6]
Features[edit]
Avidemux is capable of non-linear video editing, applying visual effects (called 'Filters' by Avidemux) to video, and transcoding video into various formats. Some of the filters were ported from MPlayer and Avisynth. Avidemux can also insert audio streams into a video file (an action known as multiplexing or 'muxing') or extract audio streams from video files (an action known as 'demuxing').
Avidemux Mp4 Vs Mp4v2
An integral and important part of the design of the program is its project system, which uses the SpiderMonkey JavaScript engine. Whole projects with all options, configurations, selections, and preferences can be saved into a project file. Like VirtualDub's VCF scripting capabilities, Avidemux has advanced scripting available for it both in its GUI and command line modes. It also supports a non-project system just like VirtualDub, where users can simply create all of their configurations and save the video directly without making a project file. A project queue system is also available.
Avidemux has built-in subtitle processing, both for optical character recognition of DVD subtitles and for rendering hard subtitles. Avidemux supports various subtitle formats, including MicroDVD (.SUB), SubStation Alpha (.SSA), Advanced SubStation Alpha (.ASS) and SubRip (.SRT).
Components[edit]
Avidemux was written from scratch, but additional code from FFmpeg, MPlayer, Transcode and Avisynth has been used on occasion as well. Nonetheless it is a completely standalone program that does not require any other programs to read, decode, or encode other than itself. The built-in libavcodec library from the FFmpeg project is used for decoding and encoding of various audio and video formats such as MPEG-4 ASP. The primary (though not the only) Avidemux programmer uses the nickname 'Mean' on the Avidemux forum.[7]
Multithreading[edit]
Multithreading has been implemented in the following areas of Avidemux (some partially through libavcodec):
- Encoding
- MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 (using libavcodec)
- MPEG-4 Part 2 SP/ASP (using libavcodec or Xvid)
- Earlier versions of Xvid are not compatible with this feature.
- H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 AVC (using x264)
- H.265/HEVC (using x265)
- Decoding
- MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 (using libavcodec)
- MPEG-4 Part 2 SP/ASP (using libavcodec)
Supported formats[edit]
Avidemux Mp4v2
Avidemux supports following file formats:
| Name | File extension | As input | As output |
|---|---|---|---|
| Audio Video Interleave | .AVI | Yes | Yes |
| Advanced Systems Format | .ASF, .WMV and .WMA | Yes | No |
| Flash Video | .FLV | Yes | Yes |
| Matroska | .MKV | Yes | Yes |
| MPEG elementary stream | N/A | Yes | No |
| MPEG program stream | .MPG and .MPEG | Yes | Yes[a] |
| MPEG transport stream | .TS | Yes | Yes |
| MPEG-4 Part 14 | .MP4 | Yes | Yes |
| NuppelVideo | .NUV | Yes | No |
| OGM | .OGM | Yes | Yes |
| QuickTime | .MOV | Yes | No |
| 3GP | .3GP | Yes | No |
| DVD-Video | .VOB | Yes | Yes |
| WebM | .WebM | Yes | Yes |
| Name | As input | As output |
|---|---|---|
| AV1 | Yes[b] | No |
| Cinepak | Yes | No |
| DV | Yes | Yes |
| FFV1 | Yes | Yes |
| H.263 | Yes | Yes |
| H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 AVC | Yes | Yes[c] |
| H.265/HEVC | Yes | Yes[d] |
| HuffYUV | Yes | Yes |
| MPEG-1 | Yes | Yes |
| MPEG-2 | Yes | Yes |
| MPEG-4 Part 2[e] | Yes[f] | Yes[g] |
| Motion JPEG | Yes | Yes |
| MSMPEG-4 v2[h] | Yes | No |
| Raw video – RGB | Yes | No |
| Raw video – YV12 | Yes | Yes |
| Snow | No | Yes |
| Sorenson Video 3 (SVQ3) | Yes | Yes |
| VC-1[i] | Yes | No |
| VP3 | Yes | No |
| VP6 | Yes[j] | No |
| VP8 | Yes[j] | No |
| VP9 | Yes[j] | Yes[k] |
| Windows Media Video 8[l] | Yes | No |
| Y800 | Yes | Yes |
| Name | As input | As output |
|---|---|---|
| Adaptive Multi-Rate – Narrow Band (AMR-NB) | Yes | No |
| Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) | Yes | Yes |
| AC-3 | Yes | Yes |
| DTS | Yes | No |
| Linear pulse-code modulation (LPCM) | No | Yes |
| MP2 | Yes | Yes |
| MP3 | Yes | Yes |
| Opus | Yes | Yes |
| Pulse-code modulation (PCM) | No | Yes |
| Vorbis | Yes | Yes |
| Name | File extension | As input | As output |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows bitmap | .BMP | Yes | No |
| JPEG | .JPG and .JPEG | Yes | No |
See also[edit]
Notes[edit]
- ^Can create files that are compatible with Video CD, SVCD or DVD Video
- ^Using libaom
- ^Using x264
- ^Using x265
- ^Both Simple Profile and Advanced Simple Profile
- ^Supported codec FourCCs: DIVX, DX50, XVID, FMP4, M4S2
- ^Using FFmpeg or Xvid
- ^FourCC: DIV3
- ^FourCC: WMV3
- ^ abcThrough libavcodec
- ^Using Libvpx
- ^FourCC: WMV2
References[edit]
- ^Avidemux 2.5 Change Log (included with the Avidemux 2.5.5 for Windows)
- ^'Avidemux 2.7.8'. SourceForge. Dice Holdings. Retrieved 15 July 2020.
- ^Avidemux developers (12 November 2012). 'Avidemux Quickstart'. avidemux.org. Archived from the original on 12 September 2020. Retrieved 12 September 2020.
Avidemux is a simple tool for simple video processing tasks. The keyword here is simple: it does not offer tools like a timeline, multitrack editing, you cannot freely move or splice audio and video clips from various sources. However, Avidemux allows you to do elementary things in a very straightforward way.
- ^'FreeBSD Avidemux port'. Archived from the original on 15 April 2013. Retrieved 2 July 2010.
- ^'The NetBSD Packages Collection: multimedia/avidemux'. Retrieved 2 July 2010.
- ^'OpenBSD Packages'. Archived from the original on 10 February 2010. Retrieved 2 July 2010.
- ^'Messages by 'Mean''. Avidemux forum. Retrieved 19 November 2011.
- ^ ab'Supported input formats'. Avidemux wiki documentation. Avidemux. 16 April 2010. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^ ab'Supported output formats'. Avidemux wiki documentation. Avidemux. 15 April 2010. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^'Video decoders'. Avidemux wiki documentation. Avidemux. 16 April 2010. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^'Video encoders'. Avidemux wiki documentation. Avidemux. 15 April 2010. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^'Audio decoders'. Avidemux wiki documentation. Avidemux. 16 April 2010. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- ^'Audio encoders'. Avidemux wiki documentation. Avidemux. 15 April 2010. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
Further reading[edit]
- Rankin, Kyle (2006). Linux Multimedia Hacks. O'Reilly Media, Inc. pp. 189–190, 221–222. ISBN978-0-596-10076-6.
- Montabone, Sebastian (2010). 'Chapter 10: Movie Editing'. Beginning Digital Image Processing: Using Free Tools for Photographers. Apress. pp. 235–253. ISBN978-1-4302-2841-7.
External links[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Avidemux. |
Avidemux Mp4 Mp4v2
Avidemux Mp4v2 Vs Mp4
I'm sorry if this question has been asked before...I'm just trying to export a clip of an MP4 in Avidemux. When I go to 'save video,' all I see are 'all files' under file type. Can't you export it to MP4 and other types? Where do I go to to do this?
I notice there's a 'format' part on the left part of the program...by default, this is AVI, so I exported it to a generic file and renamed it to an MP4. However, this just played it as an audio file. When I change the 'format' to MP4, it won't save the video file, saying there is an invalid audio stream.
If anyone can tell me how to export MP4 in Avidemux (or maybe a more painless way to simply split an MP4 file), I'm appreciative of any advice.

